Neurodegenerative diseases and Aging
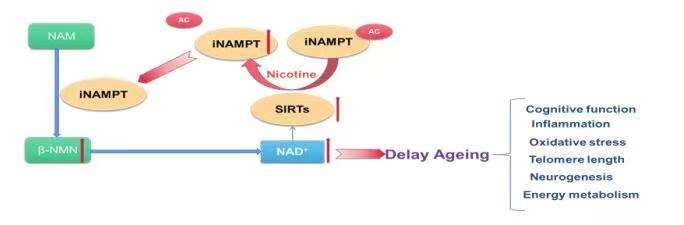
Aging is the primary risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. As the brain ages, it experiences a decline in neural function, decreased neural plasticity, and a weakened blood-brain barrier. This makes it more susceptible to damage from accumulated neurotoxic proteins like amyloid beta and tau in Alzheimer's disease or alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Furthermore, age-related decreases in neurotrophic factors and immune function can impede neuronal repair mechanisms. The result is a heightened vulnerability to neurodegeneration, leading to cognitive and motor dysfunction. Therefore, a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying the aging process is crucial for the development of effective strategies to prevent or delay neurodegenerative diseases.